The UX/UI Industry: A Beginner’s Guide

In today’s digital era, a well-designed user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) make a website or an app more engaging, trustworthy, and accessible. That is why an increasing number of companies are looking for talented user interface and user experience designers who can transform the digital presence of their business through optimized interfaces, improved usability, and human-centered design.
It should come as no surprise that User Experience Researcher and User Interface Designer are among the top 100 best jobs in America with a projected growth rate of 19% and 27% respectively, according to CNNMoney/PayScale’s Best Jobs in America.
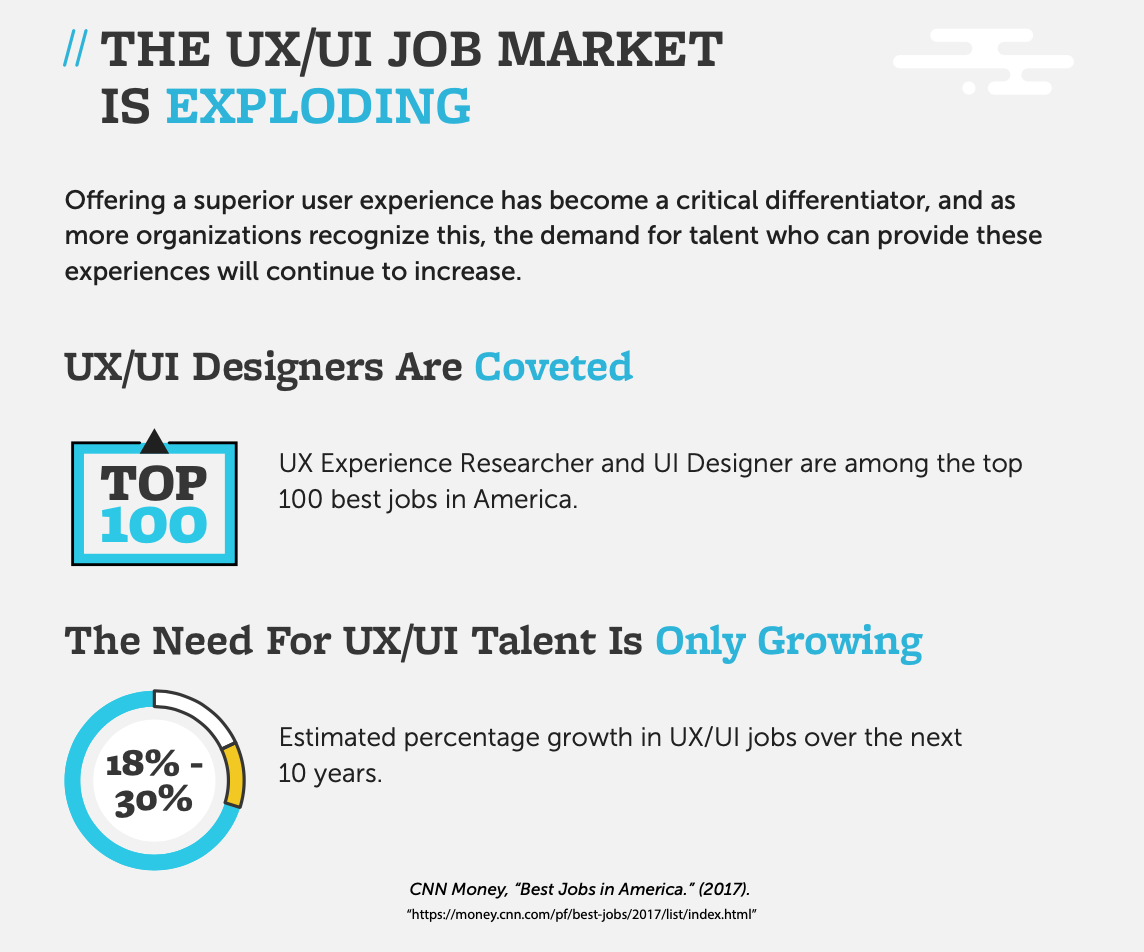
With many companies placing a stronger focus on strategic design, there has never been a better time to pursue a career in the field of UX/UI design. Having a comprehensive understanding of design and interface principles and their differences is a critical step in becoming a UX or UI designer. This article will look at the differences between UX and UI, industry examples, career pathways, and more.
What is User Experience (UX)?
Everything from the way you interact with your computer or mobile phone to the location of the buttons on your TV’s remote control are a few examples of factors that contribute to user experience. Your user experience is simply your interaction with a product, service, or technology.
The User Experience Professionals Association defines UX as an approach to product development that incorporates direct user feedback throughout the development cycle (known as human-centered design) in order to reduce costs and create products and tools that meet user needs and have a high level of usability (meaning easy to use).
Companies today enjoy many advantages by adding UX to their development processes. These benefits may include:
• Improved sales and revenue performance
• Reduced training and support costs
• Decreased development time and costs
• Reduced maintenance time and costs
• Improved customer engagement and satisfaction
What is User Interface (UI)?
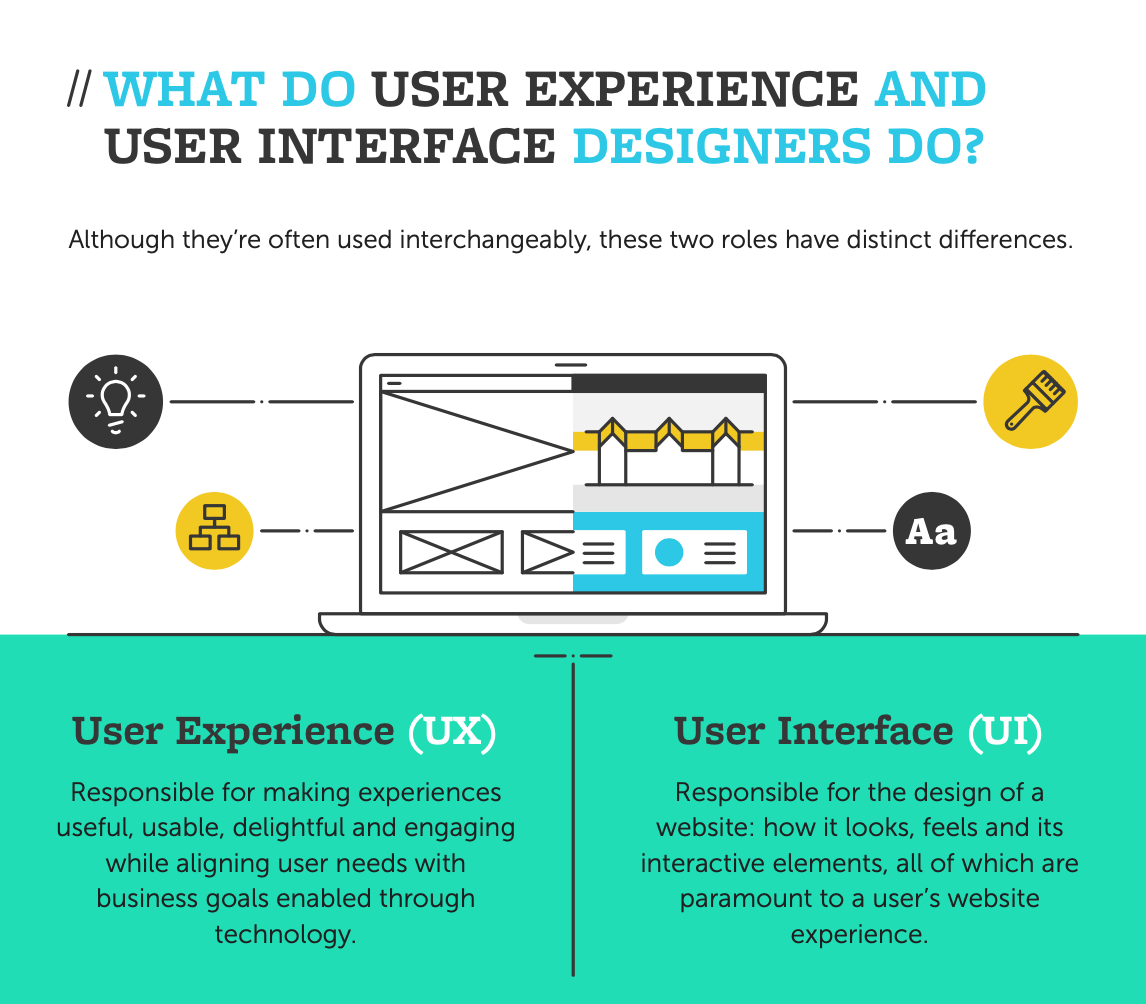
With over 1.74 billion websites on the internet today and over 4 million mobile apps available for download, user interface has become more important than ever before. Simply put, user interface is the visual design of a software or product and includes what you see, whereas user experience is what you feel. This critical design element involves predicting users’ interests and needs and building an interface that both understands and meets them. UI also optimizes the responsiveness, performance, and accessibility of the product, ensuring that it is intuitive and connects with its intended user.
Much like user experience, there are many advantages for companies to incorporate user interface design into a product. These benefits may include:
• Stronger insights from user engagement
• Reduced troubleshooting and associated costs
• Improved conversion rates and reduced abandonment
• Increased customer acquisition and loyalty
• Improved search engine optimization (SEO)
We’ve created a graphic below to illustrate the difference between User Experience and User Interface designers.
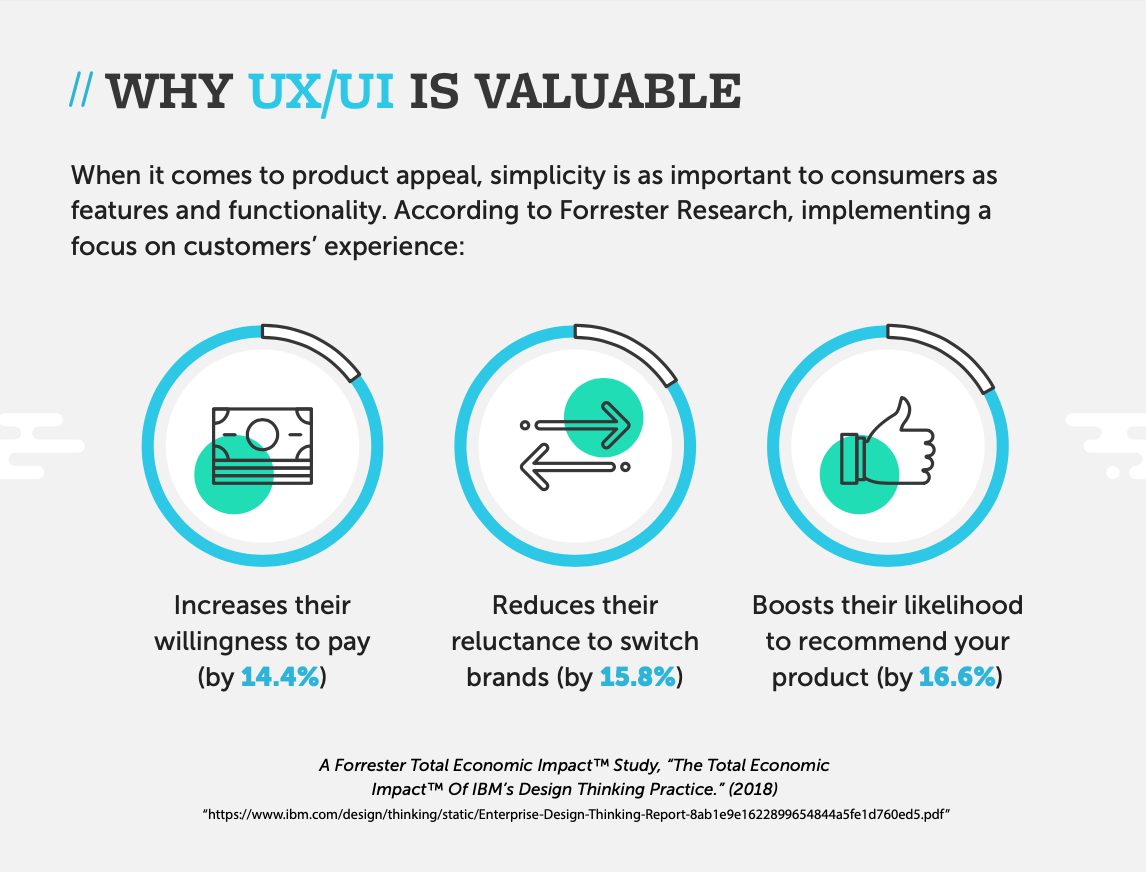
Why is UX/UI Valuable
Human behavior influences user experience and user interface. By understanding how different psychology principles influence human behavior, UX/UI professionals can design websites, products, and more to evoke precise responses and actions from users.
Think of the last website you visited. Did it load quickly? Were you able to find what you needed in a few clicks or less? Chances are, if you said no to either of those questions, you left the site. In fact, 79% of people who have a bad UX on a site leave and search for another option. UX/UI professionals understand what drives human behavior and can translate that into specific elements of a website to prevent user abandonment and promote user engagement.
Thanks to tools like Google Analytics, UX/UI designers can collect and view advanced data on how users interact with their site, where they navigate, and where they may be falling off. These insights can be used to identify areas of focus in order to improve the interface and user experience so that site visitors are more engaged and thus, more likely to stay on the page, make a purchase, or another intended action.
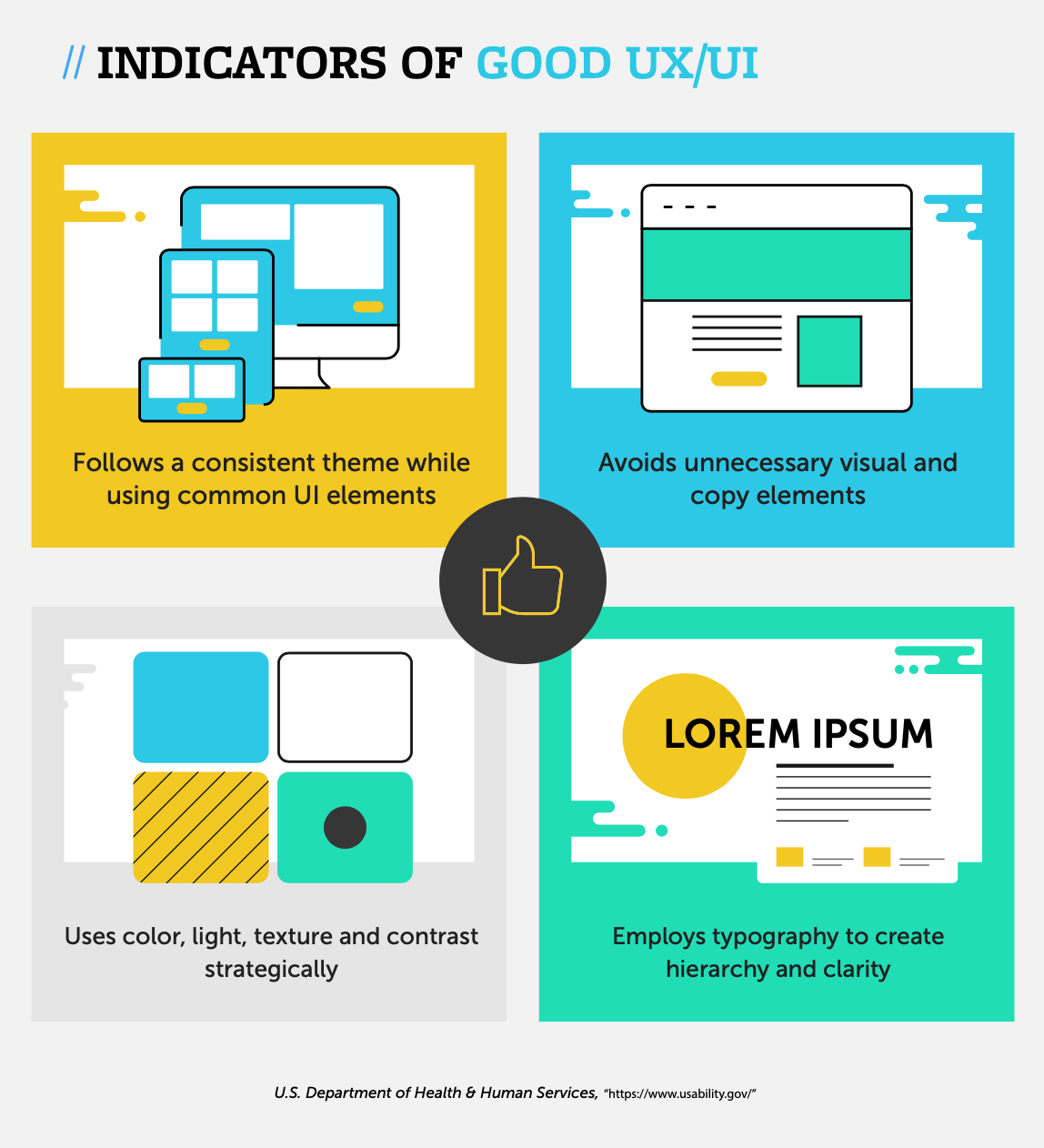
Indicators of Good UX/UI
Without a good user interface, a user might struggle to see the value in the product or service. The entire user experience of a website should be pleasing, simple, and intuitive, combining great aesthetics and functionality. Here are a few signs that indicate good UX/UI, according to Usability.gov:
• Creates consistency and uses common UI elements
• Avoids unnecessary elements and is clear in language
• Uses color, light, texture, and contrast strategically
• Uses typography to create hierarchy and clarity
How UX/UI is Important Across Industries
In any industry, a lot of thought goes into how users will interact with a product or service. User experience and user interface have a much broader reach than just websites or software. These elements apply to any product or service that involves user interaction.
Don Norman, a psychologist and usability consultant who’s worked with companies like Apple and Hewlett-Packard, is often referred to as the father of UX/UI. His book The Design of Everyday Things explores the value of designing all types of products and services — from a door handle to software — with true empathy for users.
However, UX/UI isn’t only about the user. Meeting the business goals of the product and aligning them with those of the user are just as critical, according to an article about UX and graphic design by Adobe. Ultimately, the goal of a UX or UI designer is to match business goals to user needs through a process of research, testing, and optimization. This means that good UX/UI can apply to nearly any business in any career field.
In the beginning of the digital design era, there was no such profession as a UI or UX Designer. If a company was looking for a good website to promote their service, they only had two options: a graphic designer or a webmaster. Today, UX/UI professionals can help companies increase sales, retain customers, and improve their brand value. Research estimates suggest that every dollar invested in UX brings 100 dollars in return. That’s an ROI of nearly 10,000%, and this number is continuing to grow.
Available Jobs in UX/UI
UX/UI is not only empowering customer productivity, but also the workforce by opening up new career options. With user experience and user interface becoming increasingly important to customer retention, UX/UI professionals are incredibly valuable to many modern businesses.
Let’s take a look at some of today’s in-demand jobs and career pathways in the field:
1. Product
• Product Designer
• Product Manager
2. Development
• UI Developer
• UX Developer
• UX Researcher
3. Web
• Web Designer
• Interaction Designer
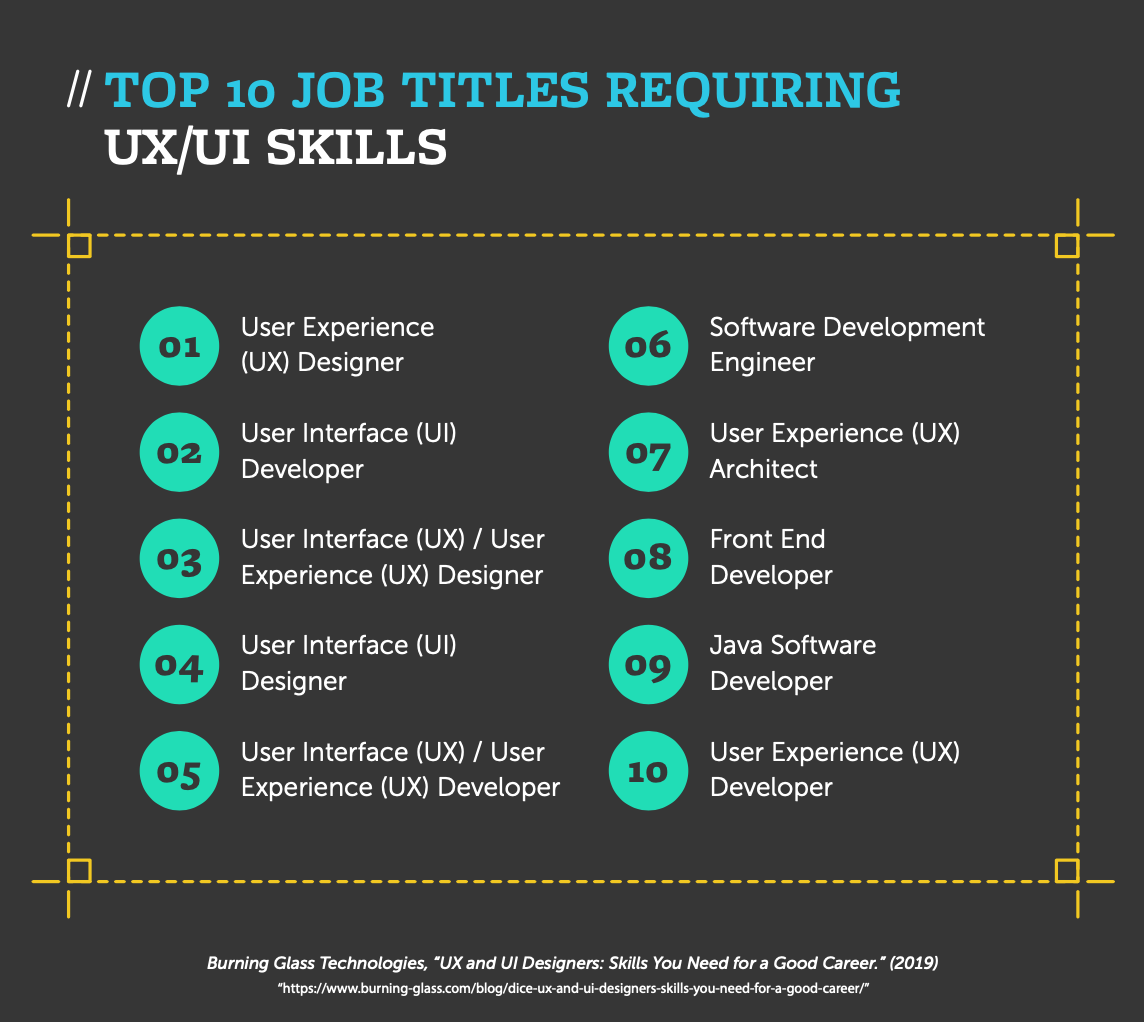
In-Demand Skills in the UX/UI Industry
Many companies today are beginning to understand the importance of a well-designed user interface and experience. With that, we see more and more of those companies requiring talented and qualified professionals who can add value to their organizations. According to data from Burning Glass Technologies, demand for UX/UI designers and developers is projected to grow by 14.9% over the next 10 years. But what skills will potential employers be looking for? In the field of UX/UI, there are a number of skills and qualities that can help set qualified professionals apart from the competition.
Below are three of the many technical skills that can help you become an in-demand and proficient UX/UI professional:
Visual Design Theory:
While an interface that functions is a distinct necessity, an interface that draws the eye of its user is just as important. It is crucial to have an understanding of color theory, iconography, typography, and other elements of visual design that modern UX/UI designers need to provide the best possible experience.
User-Centered Design:
The common theme throughout this post is the importance of designing with users in mind. That being said, how do we know who our user is? How do they act? These are questions that can be answered by delving into research techniques and methodologies such as Decision Mapping, Insight Synthesis, and Prototyping.
Front End Development:
Web design and development are divided into two categories: front end and back end. Front end code is responsible for how a website or app is displayed on screen, whereas back end code is responsible for performing all requests made via the front end. What good is a solid interface if no one can use it? It just isn’t. That is why it is a good idea for front end developers to have an understanding of UX/UI and vice-versa. UX/UI developers should understand the fundamentals of front end web design, including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in order to create full-fledged visual experiences.
Learn More About UX/UI?
Employers across many industries are looking for innovators and creative thinkers with the skills to improve their businesses through creative interfaces and engaging user experiences.
Now that you have a better understanding of how UX/UI can influence business and benefit your clients, you can learn how to leverage it to your advantage.
Are you ready to start your own UX/UI journey? Visit the Rice University UX/UI Boot Camp or contact our admissions team at to discover how you can gain the fundamentals to work in the field.
Over the course of 24 intensive weeks, you will be challenged to employ user-centric design and a wealth of creative tools to build engaging designs and user experiences. You will also walk out with an impressive professional portfolio and the confidence you need to succeed as a UX or UI professional.

 Live Chat
Live Chat